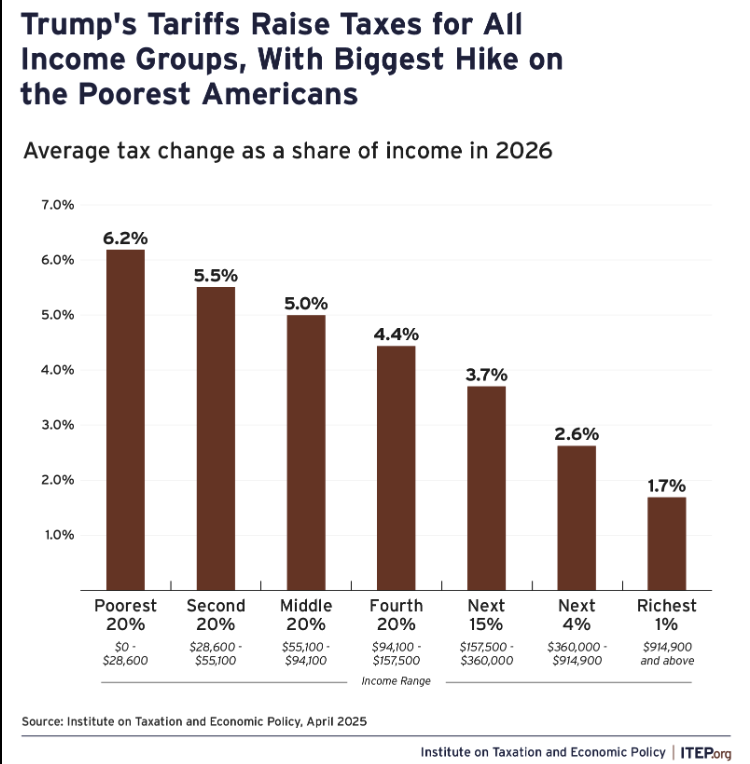
Tariffs in 2025: What Are They and What Are Their Implications?
With the recent decision of the U.S. to impose tariffs, it’s important to understand what tariffs are and their implications. Tariffs are taxes placed on foreign imports and they are used in an attempt to protect domestic jobs and businesses from being shut out by foreign markets. Tariffs can also be used as a tool for controlling international trade, this usually, however, has the negative impact of increasing the cost of goods greatly and risks creating an economic recession. It is for this reason that tariffs are a poor economic choice and should be removed.
Let’s look at the historic use of tariffs and, when we do, we see that they have never worked in the ways intended. In the 1929 stock market crash, President Herbert Hoover attempted to remedy the economic depression by enforcing a 20% tariff on agricultural and industrial goods. This, however, caused numerous countries (ie. Canada, France, and Spain) to impose retaliatory tariffs which slowed trade and caused an even greater economic recession. “The slowdown of trade weakened the US economy. By 1933, US exports dropped by 61 percent. Smoot-Hawley is often cited by experts as a factor which aggravated the US economic crisis” (Aljeezera). Tariffs have the un-ignorable effect of increasing global trading tensions by aggravating foreign nations and setting an ultimatum. Tariffs, as shown in this instance, cause the risk of a retaliatory tariff war which creates a trade stalemate; this is devastating as the US relies heavily on trade for the economy. Not only will prices for the consumer increase but there could be the ruinous effect of an economic recession happening due to slowed trade and heightened international tensions. If this situation were to repeat itself, the U.S. economy would greatly suffer and national debt would only increase. The opportunity cost of using tariffs is sacrificing good relations with other nations; the current tariffs have a high likelihood of having this effect.
Nationwide Group
General Motors (GM) closed numerous U.S. plants and laid off thousands due to Trump’s 2018 steel taxes. His tariffs cost them ~$1 billion, though tariffs may increase jobs in the distant future that doesn’t take away from the fact that, in the present, many jobs are being lost. This is especially impactful for high school students, such as me, as many people need to support their families and the risk of their parents/guardians losing their job creates more economic instability. It’s important to look at this objectively, lower and middle class people are those who suffer the most because of tariffs and make up a majority of the population, we cannot simply act without thinking of society.
Coalition on Human Needs
In addition to this, tariffs also cause many companies to move away from the U.S. markets, which is the opposite of the tariff's intended purpose as evidenced by “GM sold 835,934 cars in China and 694,638 in the U.S.” (Market Watch). The high taxes due to tariffs cause businesses to find other markets which further worsens the U.S. economy and job prospects. Instead of demand going up with a lack of supply, the scarcity and increased cost caused the businesses to look for other consumers. The economy is already suffering, the current tariffs will only cause panic and further instability.
“Considering that some of these tariffs have been placed on our allies within NATO, tariffs have the potential to not only upset our own economy, but also damage our national security interests as well” (Fordham University).
Tariffs often create economic instability for other nations- for example the Japanese automobile tariffs which caused the appreciation of the yen and a major economic depression- which then causes foreign nations to blame the country which initiated the tariffs. Many of our current tariffs are imposed on NATO allies which has the adverse threat of causing a potential
Many argue that tariffs are good because they increase U.S. jobs but, in actuality,“[tariffs] end up costing U.S. jobs on a net basis, after accounting for retaliation and higher production costs for many businesses” (Darden, University of Virginia) meaning the gain and loss is a net even. Tariffs cause instability in international relations and do not increase domestic productivity, the 1800's tariffs didn't make businesses more competitive but had the opposite effect of reducing domestic productivity by 25-35% and tariffs won’t help now. Overall, I strongly believe implementing tariffs in 2025 will have a negative impact because of the economic strife, the lack of increase in the U.S. job market, and the immense tensions they cause.